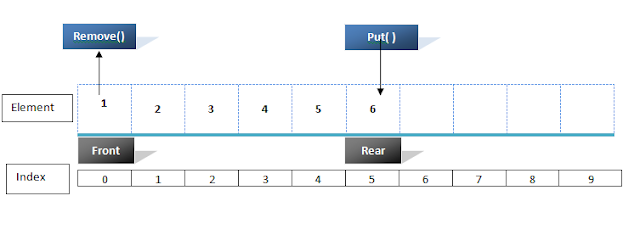
A queue is a linear list of elements in which deletions can take place only at one end, called the front of the stack, and insertion can take place only at the other end, called the rear. The term FRONT and REAR are used in describing a linear list only when it is implanted as queue. Queues are also called First in First out (FIFO) Lists. This makes the queue a First-In-First-Out (FIFO) data structure.
A queue is an example of a linear data structure. Queues provide services in computer science, transport, and operations research where various entities such as data, objects, persons, or events are stored and held to be processed later. In these contexts, the queue performs the function of a buffer. Queues are common in computer programs, where they are implemented as data structures coupled with access routines, as an abstract data structure or in object-oriented languages as classes. Common implementations are circular buffers and linked lists.
Remove ( ) : Deletes an element from the front of the queue.
Queue
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| public interface Queue<T> { | |
| public boolean isEmpty(); | |
| public T remove(); | |
| public void put(T ele); | |
| public int size(); | |
| public T getFrontElement(); | |
| public T getRearElement(); | |
| } |
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| public class ArrayQueue<T> implements Queue<T> { | |
| T[] element; | |
| int front = 0; | |
| int rear = 0; | |
| private int maxSize; | |
| /** | |
| * @param initialCapacity initialize the array | |
| */ | |
| public ArrayQueue(int initialCapacity) { | |
| element = (T[]) new Object[initialCapacity]; | |
| front = 0; | |
| rear = 0; | |
| maxSize = initialCapacity; | |
| } | |
| /** | |
| * @return true iff queue is empty | |
| */ | |
| public boolean isEmpty() { | |
| return (front == rear); | |
| } | |
| /** | |
| * @return and remove front element of queue | |
| */ | |
| public T remove() { | |
| if (isEmpty()) { | |
| System.out.println("Queue is empty"); | |
| return null; | |
| } else { | |
| front = (front + 1) % maxSize; | |
| T t = element[front]; | |
| element[front] = null; | |
| return t; | |
| } | |
| } | |
| /** | |
| * put Element to the rear of the queue | |
| * | |
| * @param ele | |
| */ | |
| public void put(T ele) { | |
| int rear1 = (rear + 1) % maxSize; | |
| if (rear1 != front) { | |
| rear = rear1; | |
| element[rear] = ele; | |
| } else { | |
| System.out.println("Queue is full"); | |
| } | |
| } | |
| /** | |
| * @return array size | |
| */ | |
| public int size() { | |
| return (maxSize + rear - front) % maxSize; | |
| } | |
| /** | |
| * @return front element of the queue | |
| */ | |
| public T getFrontElement() { | |
| if (isEmpty()) { | |
| System.out.println("Queue is empty"); | |
| return null; | |
| } else { | |
| return element[(front + 1) % maxSize]; | |
| } | |
| } | |
| /** | |
| * @return rear element of the queue | |
| */ | |
| public T getRearElement() { | |
| if (isEmpty()) { | |
| System.out.println("Queue is empty"); | |
| return null; | |
| } else { | |
| return element[rear]; | |
| } | |
| } | |
| /** | |
| * @param args | |
| */ | |
| public static void main(String args[]) { | |
| ArrayQueue<Integer> aq = new ArrayQueue<Integer>(4); | |
| aq.put(1); | |
| aq.put(2); | |
| aq.put(3); | |
| aq.put(4); | |
| aq.put(5); | |
| while (!aq.isEmpty()) { | |
| System.out.println(aq.remove()); | |
| } | |
| System.out.println(); | |
| } | |
| } |
When you run the program, the output will be:
Queue is fullQueue is full123